Metrics
Open Service Mesh (OSM) generates detailed metrics for all services communicating within the mesh. These metrics provide insights into the behavior of services in the mesh helping users to troubleshoot, maintain and analyze their applications.
As of today OSM collects metrics directly from the sidecar proxies (Envoy). OSM provides rich metrics for incoming and outgoing traffic for all services in the mesh. With these metrics the user can get information about the overall volume of traffic, errors within traffic and the response time for requests.
Prometheus
To facilitate gathering of consistent traffic metrics and statistics across all services in the mesh, OSM relies on Prometheus. Prometheus is an open-source monitoring and alerting toolkit which is commonly used (but not limited to) on Kubernetes and Service Mesh environments.
Each service that is part of the mesh has an Envoy sidecar and is capable of exposing metrics (proxy metrics) in Prometheus format. Further every service that is a part of the mesh has Prometheus annotations, which makes it possible for the Prometheus server to scrape the service dynamically. This mechanism automatically enables scraping of metrics whenever a new namespace/pod/service is added to the mesh.
Deployment and Installation
OSM is able to automatically provision Prometheus and Grafana instances to monitor the mesh, however the user can choose not to, in favour of an already existing deployment or service (we will refer to the latter as Bring-Your-Own, or BYO)
Automatic bring up
By default, both Prometheus and Grafana are disabled.
However, when configured with the --deploy-grafana flag, OSM installation will deploy a Prometheus instance to scrape the sidecar’s metrics endpoints. Based on the metrics scraping configuration set by the user, OSM will annotate pods part of the mesh with necessary metrics annotations to have Prometheus reach and scrape the pods to collect relevant metrics. To install Grafana for metrics visualization, set the deploy-grafana flag to true when installing OSM using the osm install command.
The automatic bring up can be overridden with the osm install option during install time:
osm install --help
This command installs an osm control plane on the Kubernetes...
...
--deploy-prometheus Enable Prometheus deployment (default false)
--deploy-grafana Enable Grafana deployment (default false)
...
BYO (Bring-your-own)
The following section will document the additional steps needed to allow an already running instance to poll the endpoints of an OSM mesh.
List of Prerequisites
- Already running an accessible Prometheus instance outside of the mesh.
- A running OSM control plane instance, deployed without metrics stack.
- OSM controls the Envoy’s Prometheus listener aperture through
prometheus_scraping: "true", under OSM configmap. By default this is set to true, but do double check it has been enabled on the OSM configmap, or else Prometheus might not be able to reach the pods.
- OSM controls the Envoy’s Prometheus listener aperture through
- We will assume having Grafana reach Prometheus, exposing or forwarding Prometheus or Grafana web ports and configuring Prometheus to reach Kubernetes API services is taken care of or otherwise out of the scope of these steps.
Configuration
- Make sure the Prometheus instance has appropriate RBAC rules to be able to reach both the pods and Kubernetes API - this might be dependent on specific requirements and situations for different deployments:
- apiGroups: [""]
resources: ["nodes", "nodes/proxy", "nodes/metrics", "services", "endpoints", "pods", "ingresses", "configmaps"]
verbs: ["list", "get", "watch"]
- apiGroups: ["extensions"]
resources: ["ingresses", "ingresses/status"]
verbs: ["list", "get", "watch"]
- nonResourceURLs: ["/metrics"]
verbs: ["get"]
- If desired, use the Prometheus Service definition to allow Prometheus to scrape itself:
annotations:
prometheus.io/scrape: 'true'
prometheus.io/port: '<API port for prometheus>' # Depends on deployment - OSM automatic deployment uses 7070 by default, controlled by `values.yaml`
- Amend Prometheus’ configmap to reach the pods/Envoy endpoints. OSM automatically appends the port annotations to the pods and takes care of pushing the listener configuration to the pods for Prometheus to reach:
- job_name: 'kubernetes-pods'
kubernetes_sd_configs:
- role: pod
relabel_configs:
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_scrape]
action: keep
regex: true
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_path]
action: replace
target_label: __metrics_path__
regex: (.+)
- source_labels: [__address__, __meta_kubernetes_pod_annotation_prometheus_io_port]
action: replace
regex: ([^:]+)(?::\d+)?;(\d+)
replacement: $1:$2
target_label: __address__
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_namespace]
action: replace
target_label: source_namespace
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_name]
action: replace
target_label: source_pod_name
- regex: '(__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_app)'
action: labelmap
replacement: source_service
- regex: '(__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_osm_envoy_uid|__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_pod_template_hash|__meta_kubernetes_pod_label_version)'
action: drop
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_controller_kind]
action: replace
target_label: source_workload_kind
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_controller_name]
action: replace
target_label: source_workload_name
- source_labels: [__meta_kubernetes_pod_controller_kind]
action: replace
regex: ^ReplicaSet$
target_label: source_workload_kind
replacement: Deployment
- source_labels:
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_controller_kind
- __meta_kubernetes_pod_controller_name
action: replace
regex: ^ReplicaSet;(.*)-[^-]+$
target_label: source_workload_name
Configuring Prometheus metrics scraping
Metrics scraping can be configured using the osm metrics command. By default, OSM does not configure metrics scraping for pods in the mesh. Metrics scraping can be enabled or disabled at namespace scope such that pods belonging to configured namespaces can be enabled or disabled for scraping metrics.
For metrics to be scraped, the following prerequisites must be met:
- The namespace must be a part of the mesh, ie. it must be labeled with the
openservicemesh.io/monitored-bylabel with an appropriate mesh name. This can be done using theosm namespace addcommand. - A running service able to scrap Prometheus endpoints. OSM provides configuration for an automatic bringup of Prometheus; alternatively users can bring their own Prometheus.
- The
prometheus_scrapingconfig key in osm-controller’sosm-configConfigMap must be set to"true", which is the default configuration.
To enable one or more namespaces for metrics scraping:
osm metrics enable --namespace test
osm metrics enable --namespace "test1, test2"
To disable one or more namespaces for metrics scraping:
osm metrics disable --namespace test
osm metrics disable --namespace "test1, test2"
Custom Metrics
To implement the SMI metrics spec, OSM adds a custom WebAssembly extension to each Envoy proxy which generates the following statistics for HTTP traffic:
osm_request_total: A counter incremented for each request made by the proxy. This can be queried to determine success and failure rates of services in the mesh.
osm_request_duration_ms: A histogram representing the duration of requests made by the proxy in milliseconds. This can be queried to determine the latency between services in the mesh.
Both metrics have the following labels:
source_kind: The Kubernetes resource kind of the workload making the request, e.g. Deployment, DaemonSet, etc.
destination_kind: The Kubernetes resource kind of the workload handling the request, e.g. Deployment, DaemonSet, etc.
source_name: The Kubernetes name of the workload making the request.
destination_name: The Kubernetes name of the workload handling the request.
source_pod: The Kubernetes name of the pod making the request.
destination_pod: The Kubernetes name of the pod handling the request.
source_namespace: The Kubernetes namespace of the workload making the request.
destination_namespace: The Kubernetes namespace of the workload handling the request.
In addition, the osm_request_total metric has a response_code label representing the HTTP status code of each request, e.g. 200, 404, etc.
Known Gaps
- HTTP requests that invoke a local response from Envoy have “unknown”
destination_*labels on metrics.- In the demo, this includes requests from the bookthief to the bookstore.
- Metrics are only recorded for traffic where both endpoints are part of the mesh. Ingress and egress traffic do not have statistics recorded.
- Metrics are recorded in Prometheus with all instances of ‘-’ and ‘.’ in tags converted to ‘_’. This is because proxy-wasm adds tags to metrics through the name of the metric and Prometheus does not allow ‘-’ or ‘.’ in metric names, so Envoy converts them all to ‘_’ for the Prometheus format. This means a pod named ‘abc-123’ is labeled in Prometheus as ‘abc_123’ and metrics for pods ‘abc-123’ and ‘abc.123’ would be tracked as a single pod ‘abc_123’ and only distinguishable by the ‘instance’ label containing the pod’s IP address.
Querying metrics from Prometheus
Before you begin
Ensure that you have followed the steps to run OSM Demo
Querying proxy metrics for request count
- Verify that the Prometheus service is running in your cluster
- In kubernetes, execute the following command:
kubectl get svc osm-prometheus -n osm-system
- In kubernetes, execute the following command:
- Open up the Prometheus UI
- Ensure you are in root of the repository and execute the following script:
./scripts/port-forward-prometheus.sh - Visit the following url http://localhost:7070 in your web browser
- Ensure you are in root of the repository and execute the following script:
- Execute a Prometheus query
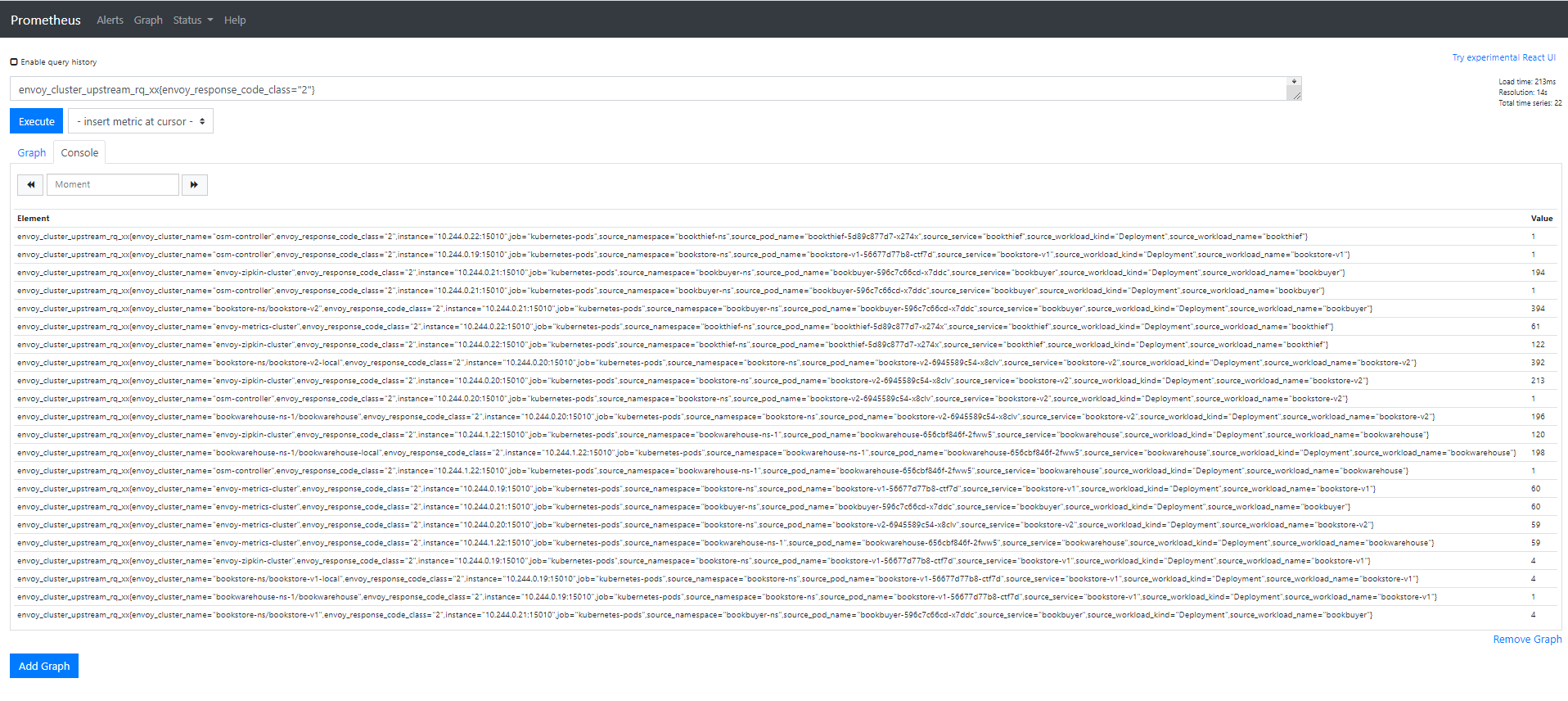
- In the “Expression” input box at the top of the web page, enter the text:
envoy_cluster_upstream_rq_xx{envoy_response_code_class="2"}and click the execute button - This query will return the successful http requests
- In the “Expression” input box at the top of the web page, enter the text:
Sample result will be:
Grafana
Grafana is an open source visualization and analytics software. It allows you to query, visualize, alert on, and explore your metrics.
Grafana uses Prometheus as backend timeseries database. If Grafana and Prometheus are chosen to be deployed through OSM installation, necessary rules will be set upon deployment for them to interact. Conversely, on a BYO model this will have to be taken care of by the user.
OSM provides some pre-cooked Grafana dashboards to display and track services related information captured by Prometheus:
- OSM Data Plane
- OSM Service to Service Metrics: This dashboard lets you view the traffic metrics from a given source service to a given destination service
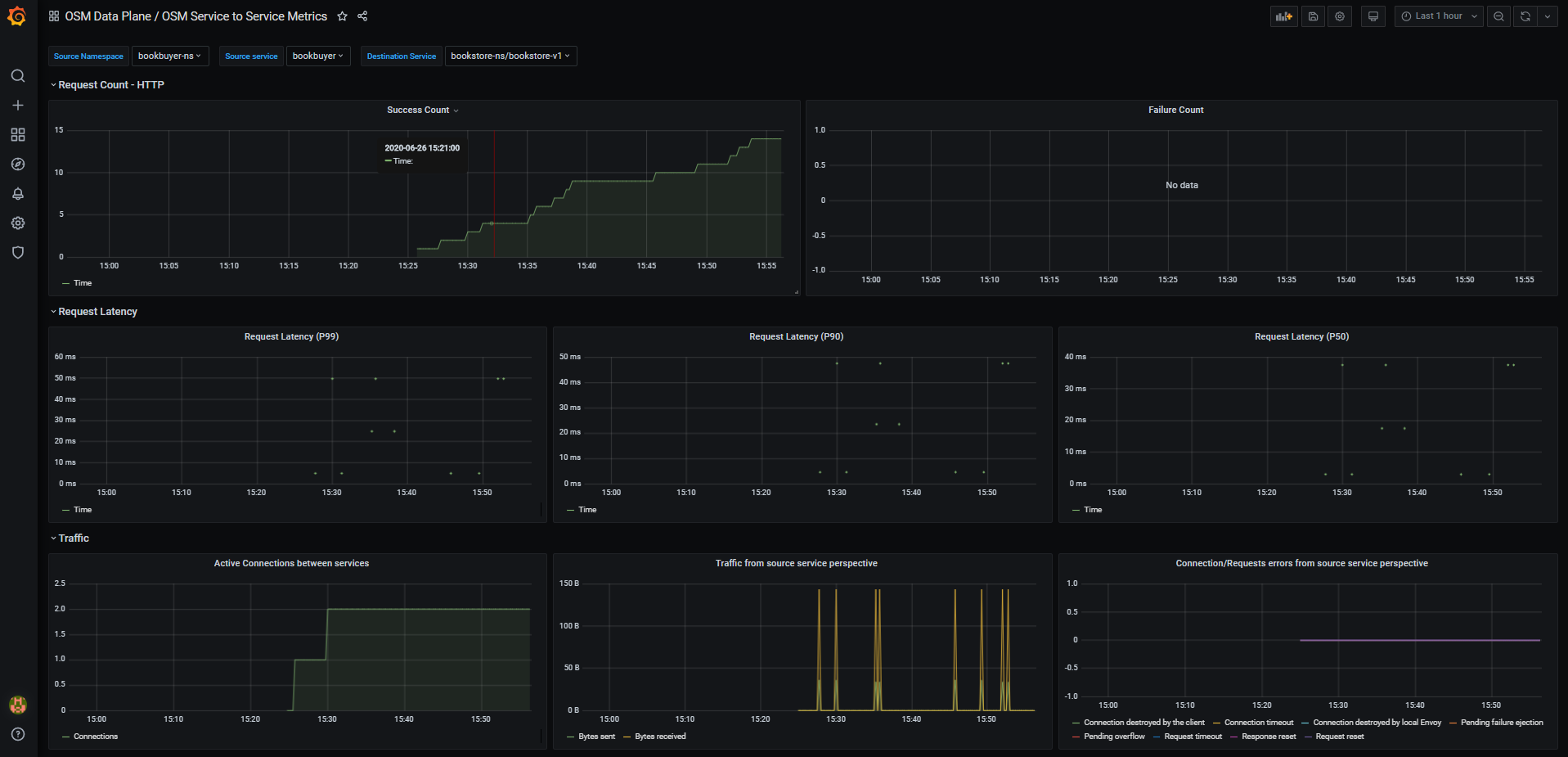
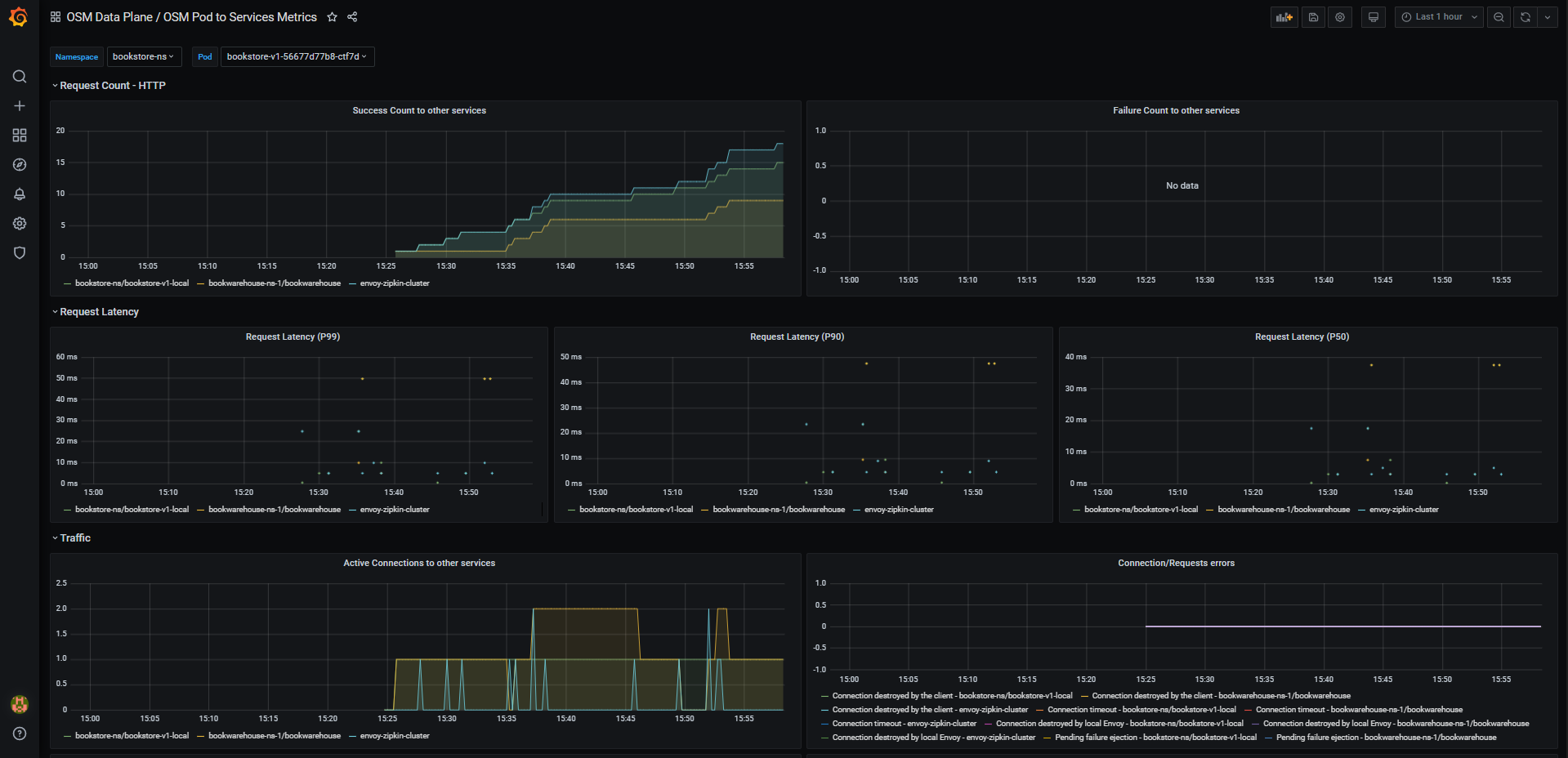
- OSM Pod to Service Metrics: This dashboard lets you investigate the traffic metrics from a pod to all the services it connects/talks to
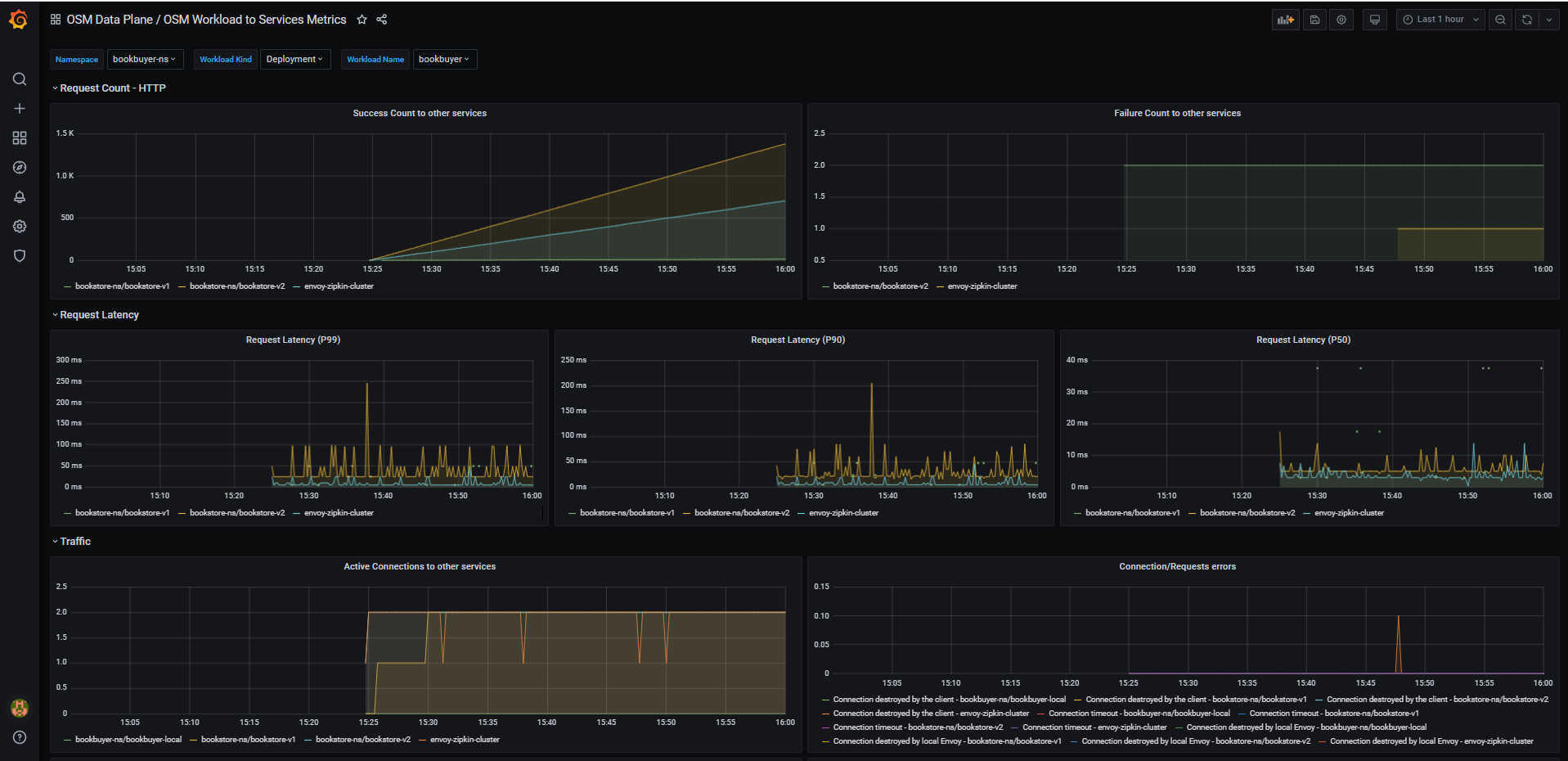
- OSM Workload to Service Metrics: This dashboard provides the traffic metrics from a workload (deployment, replicaSet) to all the services it connects/talks to
- OSM Service to Service Metrics: This dashboard lets you view the traffic metrics from a given source service to a given destination service
- OSM Control Plane
- OSM Control Plane Metrics: This dashboard provides traffic metrics from the given service to OSM’s control plane
- OSM Control Plane Metrics: This dashboard provides traffic metrics from the given service to OSM’s control plane
Importing Dashboards on a BYO Grafana instance
The dashboards (if desired) can be imported through several mechanism to the external Grafana instance.
The dashboards are located under osm/charts/osm/grafana/dashboards in OSM’s repo, and can be imported through Grafana web json load, or either copied or mounted on the instance itself through Kubernetes volume mounts.
Visualizing Metrics with Grafana
Before you begin
Ensure that you have followed the steps to run OSM Demo
Viewing a Grafana dashboard for service to service metrics
- Verify that the Prometheus service is running in your cluster
- In kubernetes, execute the following command:
kubectl get svc osm-prometheus -n osm-system
- In kubernetes, execute the following command:
- Verify that the Grafana service is running in your cluster
- In kubernetes, execute the following command:
kubectl get svc osm-grafana -n osm-system
- In kubernetes, execute the following command:
- Open up the Grafana UI
- Ensure you are in root of the repository and execute the following script:
./scripts/port-forward-grafana.sh - Visit the following url http://localhost:3000 in your web browser
- Ensure you are in root of the repository and execute the following script:
- The Grafana UI will request for login details, use the following default settings:
- username: admin
- password: admin
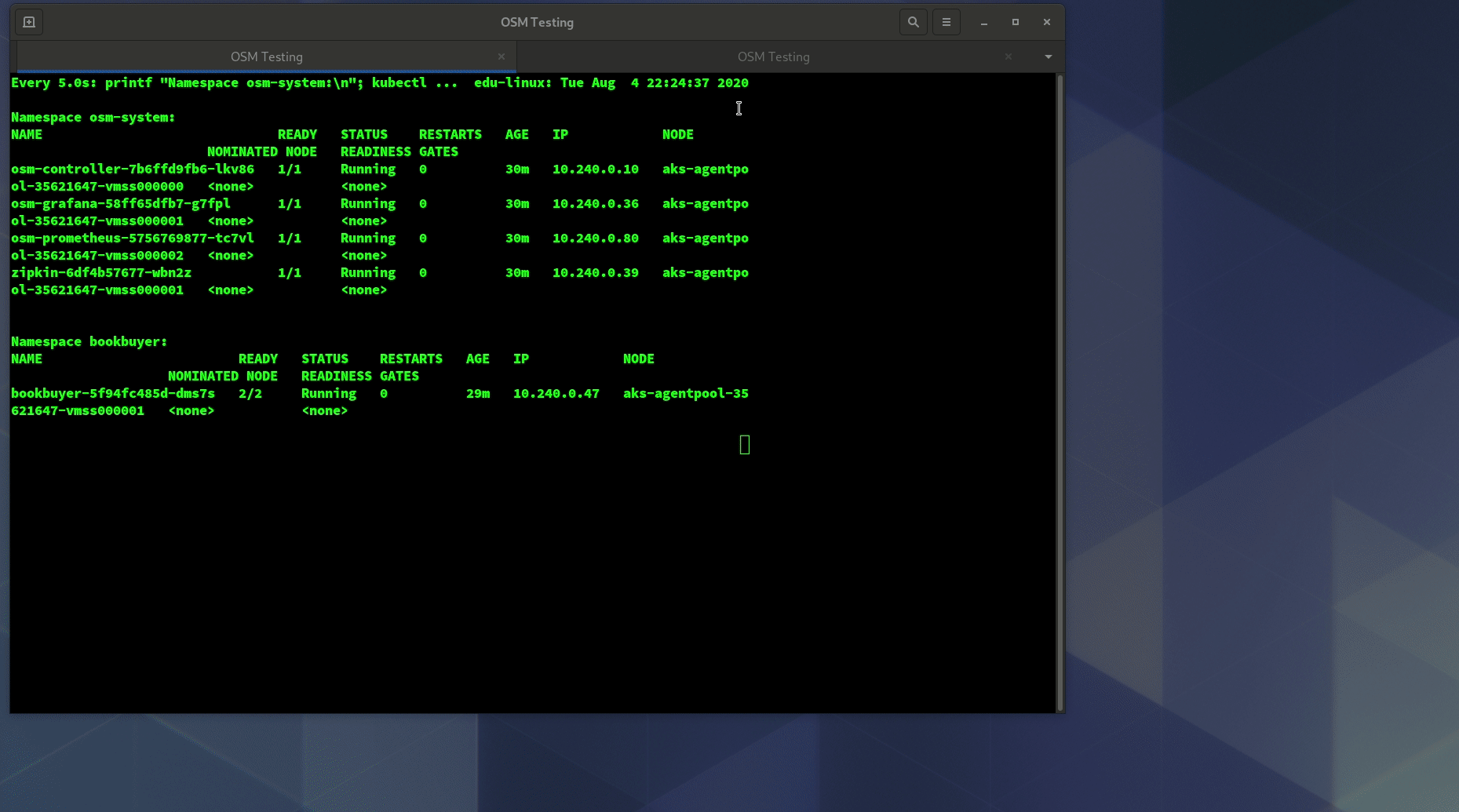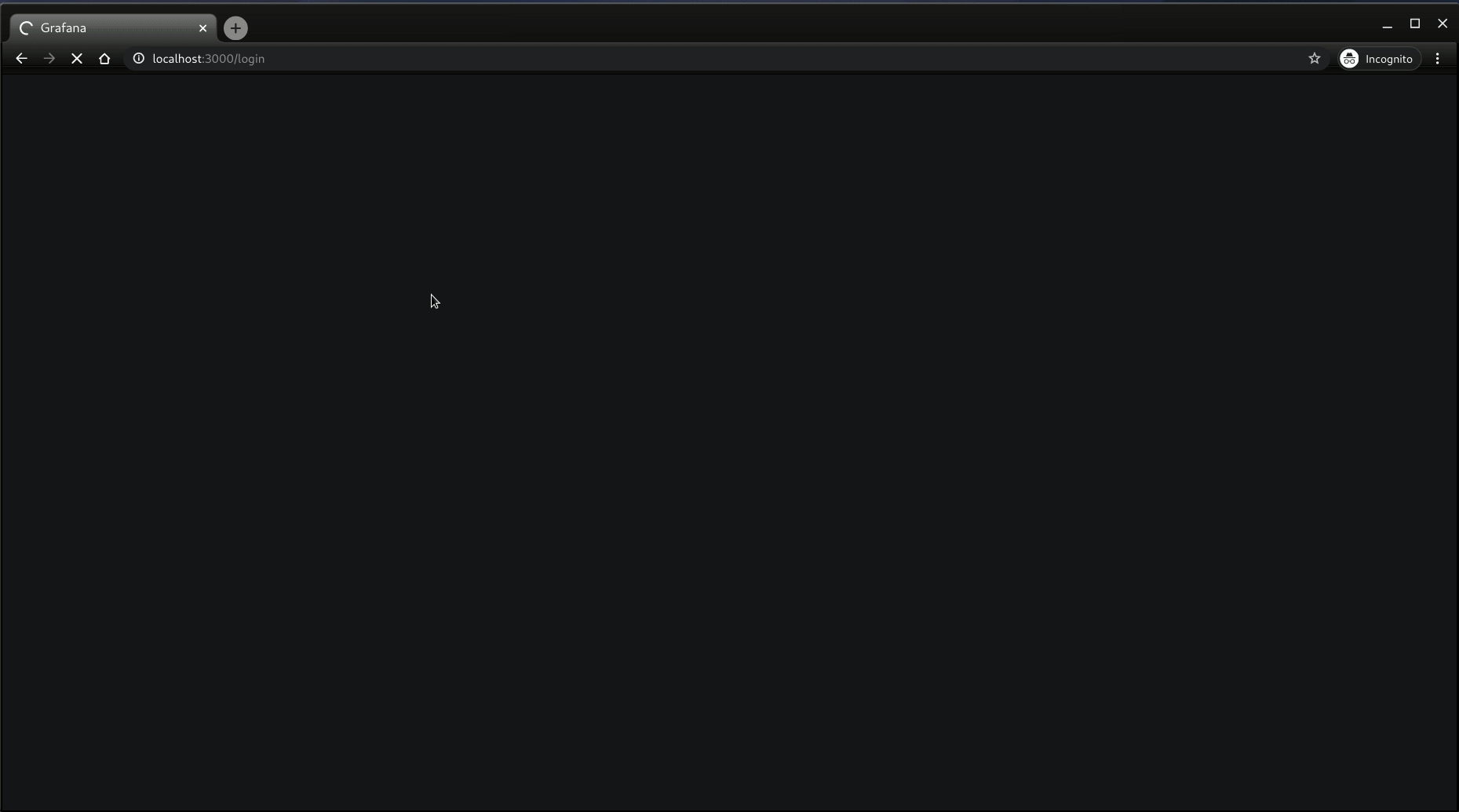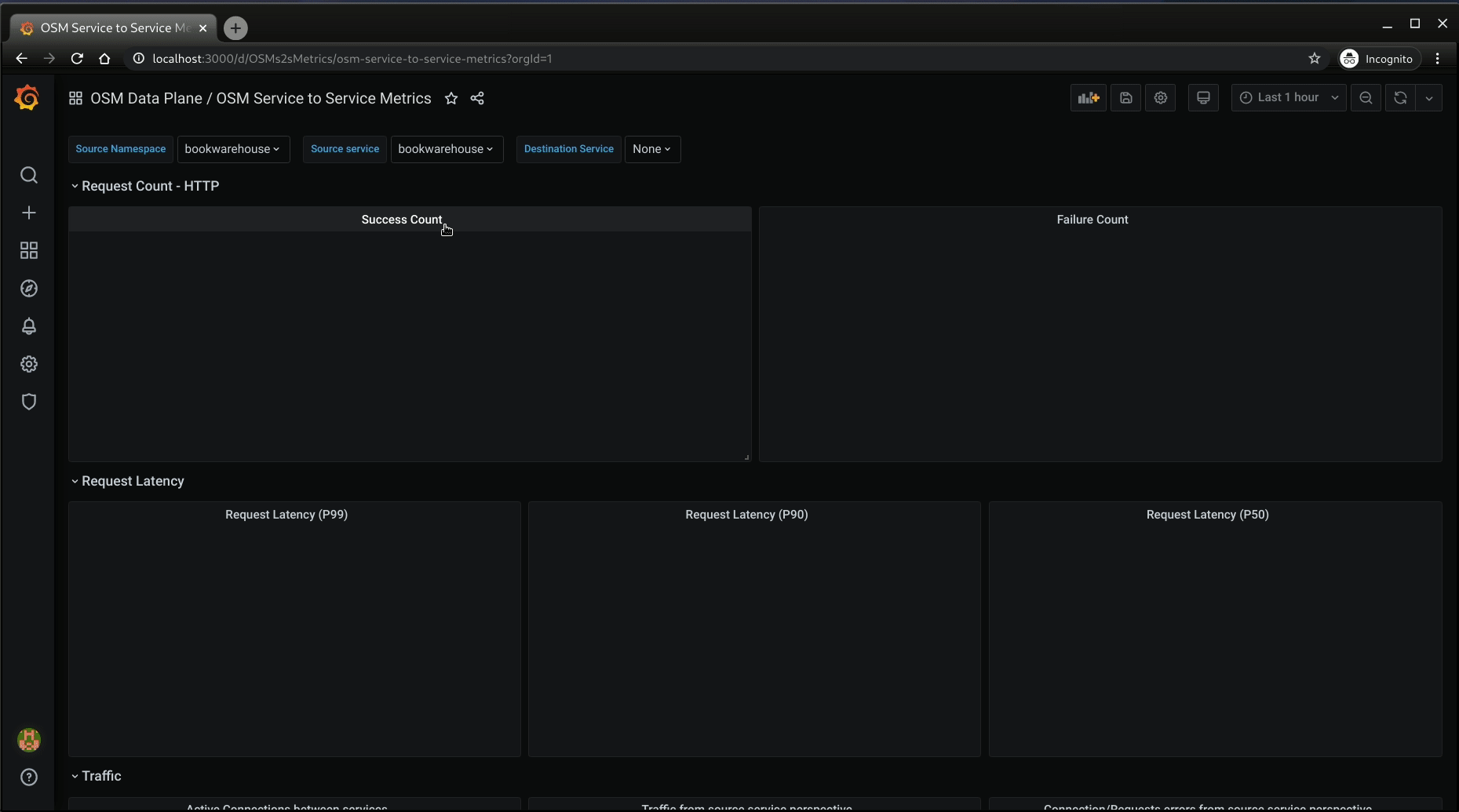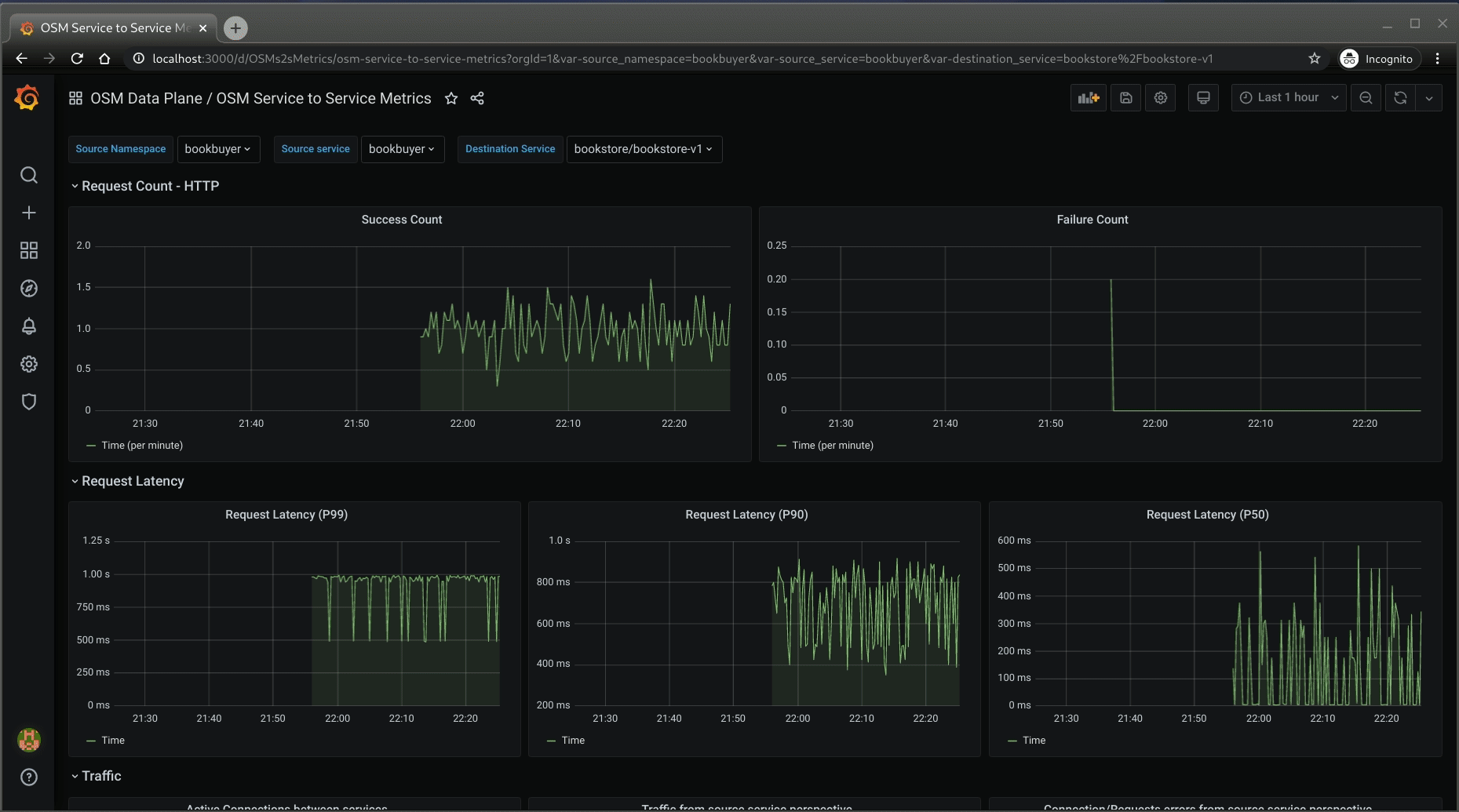
- Viewing Grafana dashboard for service to service metrics
- From the Grafana’s dashboards left hand corner navigation menu you can navigate to the OSM Service to Service Dashboard in the folder OSM Data Plane
- Or visit the following url http://localhost:3000/d/OSMs2sMetrics/osm-service-to-service-metrics?orgId=1 in your web browser
OSM Service to Service Metrics dashboard will look like:

Feedback
Was this page helpful?
Glad to hear it! Please tell us how we can improve.
Sorry to hear that. Please tell us how we can improve.